
SCIENTIFIC FILE WITH BIOLOGICAL PROOFS

SUMMARY
Important information: In this section, you will find all experiments and results in order to demonstrate, in a scientific manner, with biological proofs, the CMO tecnology eficacy. This file is presented into 5 main sections:

By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section.
Contents:
Study realised at University of Brussels, while exposing ants to Wi-Fi radiations, with CMO protection and without any protection.
Reports, synthesis, graphics.
A video movie has been recorded and you can visualise all the experiment. Fascinating..

By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section.
Contents:
Study on man of the effects of EMF with or without CMO: biological parameters taken into account: free radicals, stress resistance, stress symptoms, neurophysiology, ophtalmology.
By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section.
Contents.
Study on animal of the effects of EMF with or without CMO: parameters studied: hormonal system, cellular ion exchanges, cellular fonction, immune system, embryogenesis, neurogenesis.
By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section.
Contents:
Summarizing tables with results of studies.

By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section..
Contents:
Introducing all of the scientists who participated personally to these experiments and publications or congresses
By clicking on this title link, you will be directed to related section.
Contents:
Introducing main science publications with peer-review, participation to congresses, bibliography, works, etc..

ALL STUDIES AND EXPERIMENTATIONS WITH THEIR RESULTS
Effects of radiations from a Wi-Fi router on ants' behavir and evaluation of the compensating CMO biotechnology (CMO MF04)

It became clear that any electromagnetic field has an effect on living organisms. Many scientific papers show multiple biological effects of radiation from mobile phones (for expl.. Benlaidi and El Kharroussi, 2011; Cammaerts et al, 2011; Everaert and Bauwens, 2007; Favre, 2011; Orendaeova et al, 2009; Panagopoulos et al., 2004; Sharma and Kumar, 2010; Wang et al., 2009; Goodman et al 2003).. The authors often speak of biological stress, in general (eg Adang et al., 2009).
Moreover, Wi-Fi technology is now very widely used, and, though imperceptible to human radiation , it , nevertheless, alters undoubtedly the environment. It seemed appropriate to explore whether Wi-Fi transmitters also disrupted biological systems of living beings, observing, for example, their behavior in the absence and presence of the EM radiation.
Ants are a living biological model of choice. Their high sensitivity allows them to quickly detect the presence of undesirable elements, so small they are, in their environment. They were therefore used as a "bio-telling" system to reveal the potential adverse effect of radiation from a home Wi-Fi router, and then to test the effectiveness of a "EM compensation" biotechnology (CMO / ref . MF04). The observed behavior of the ants was
movement (their linear and angular velocity), which instantly changes following their collection of new elements, unusual, hostile or friendly to the environment.
Materials and methods
Emitter material:
This material included a NETGEAR DGN1000 brand wireless router (frequency:
2.4 GHz) whose antenna was placed at approx. 30cm from ant nests, and two PC placed 4m away from nests, exchanging data through the router for the duration of the exposure of ants.
Material "protection":
This material consists of an aluminum-cone of 5cm in diameter, containing an aqueous salt solution, treated electromagnetically (process Comosytems) emitting ultra-low bioactive signals of compensation (femtoTesla) (called CMO / MF04).
Biological material:
The experiments were performed on four experimental companies of ants : “Myrmica sabuleti” , from two colonies “ Marchin” harvested and maintained in the laboratory in polyethylene containers used as harvest area, and the edges were coated with talc to prevent the escape of ants. These ants nested in glass tubes half filled with water and cotton foam was separating ants from water. Companies were fed ad libitum with “Tenebrio Molitor” placed on a glass slide and sugar water supplied in a small stuffy cotton tube. Laboratory temperature was 20 ° C ± 1 ° C, humidity 80% and brightness of 300 lux, optimal conditions for the species.
The ants were observed and their journeys recorded as they were moving to their crop area, that is to say, on the bottom of the breeding tank and therefore in semi freedom
Experimental Protocol
Two variables were used: linear velocity (mm / sec) and the angular velocity of ants recorded and quantified as in our recent previous work (deg.ang / cm.) (Eg. Cammaerts et al, 2011) to with a new easy to use software (Cammaerts et al., 2012a in press).
Two nests were first used at the same time to perform a control in the presence of the inactive router. These nests were then exposed to EM radiation from Wi-Fi router enabled. A first test was carried out after exposure for 5 min, a second test after a 30 min exposure. (That is to say 25 min after the completion of the first test). The distance between the wireless transmitter and the ants moving area was 30 cm (see Figure 1).
Then two other unexposed still nests were used simultaneously to achieve control as before. They were then exposed to the active Wi-Fi router with a "safety net" (CMO ref MF03) placed close to the antenna transmission-reception of the router. Testing of these nests were performed first after 5 min of exposure, then after 30 min of exposure (the second test is therefore carried out 25 min after the first). The distance between the Wi-Fi antenna fitted with the "CMO protection" and the ants moving area was still 30 cm.
For each nest, trips from 10 ants were recorded and their linear and angular velocities calculated. Distributions of the values obtained were characterized by their median and quartiles, and were compared with each other using the non-parametric test Chi-Square.
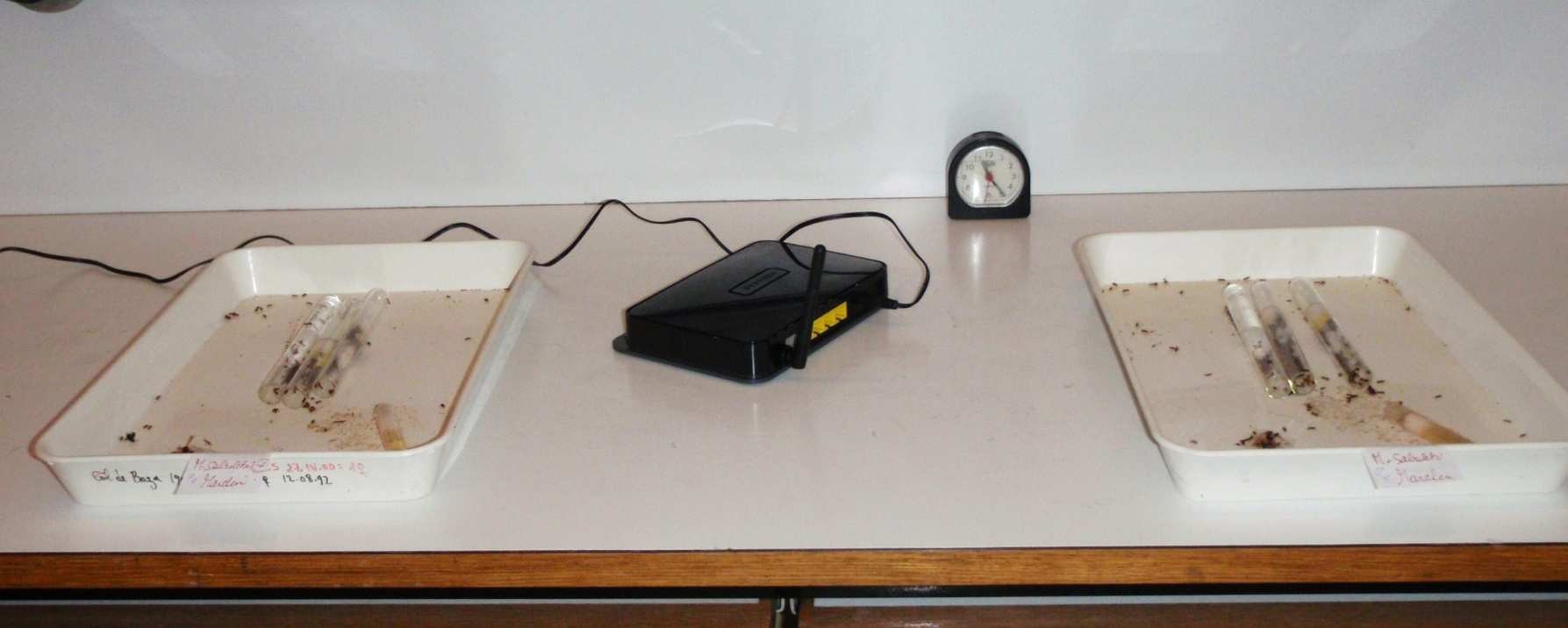



Figure 1 . Experimental configuration:
Control group) Wi-Fi "on" without CMO Wi-Fi "on" with CMO
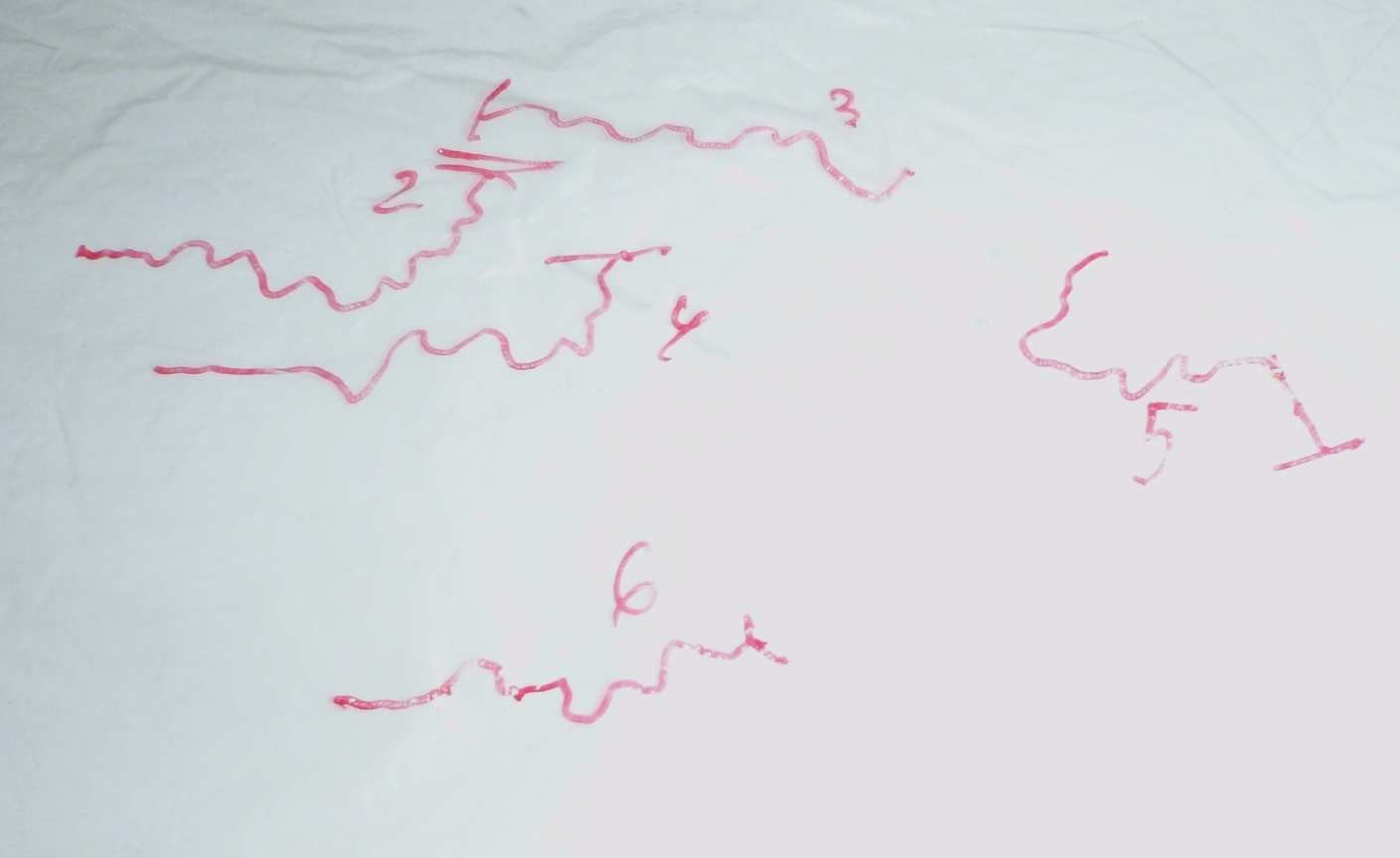
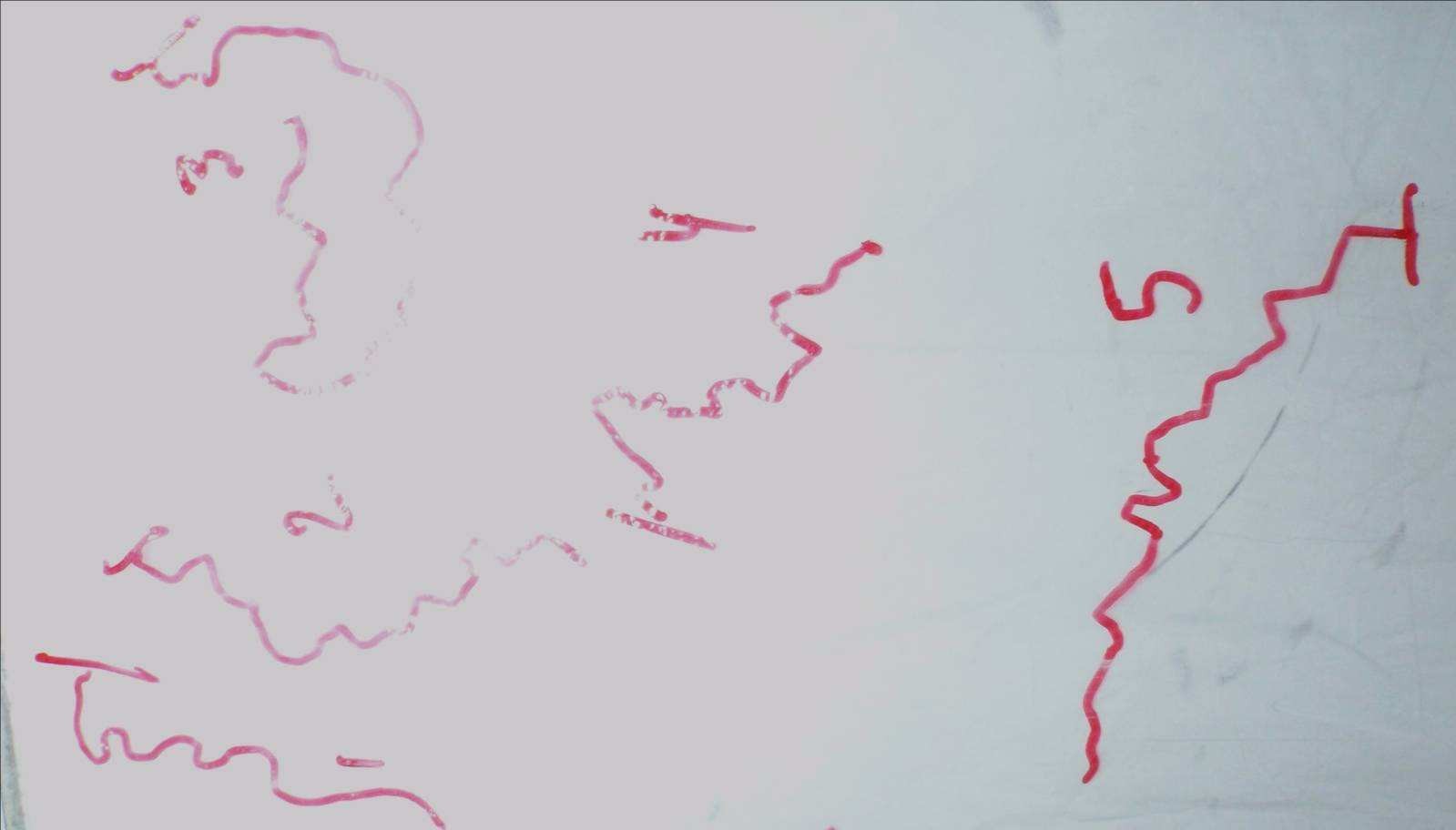

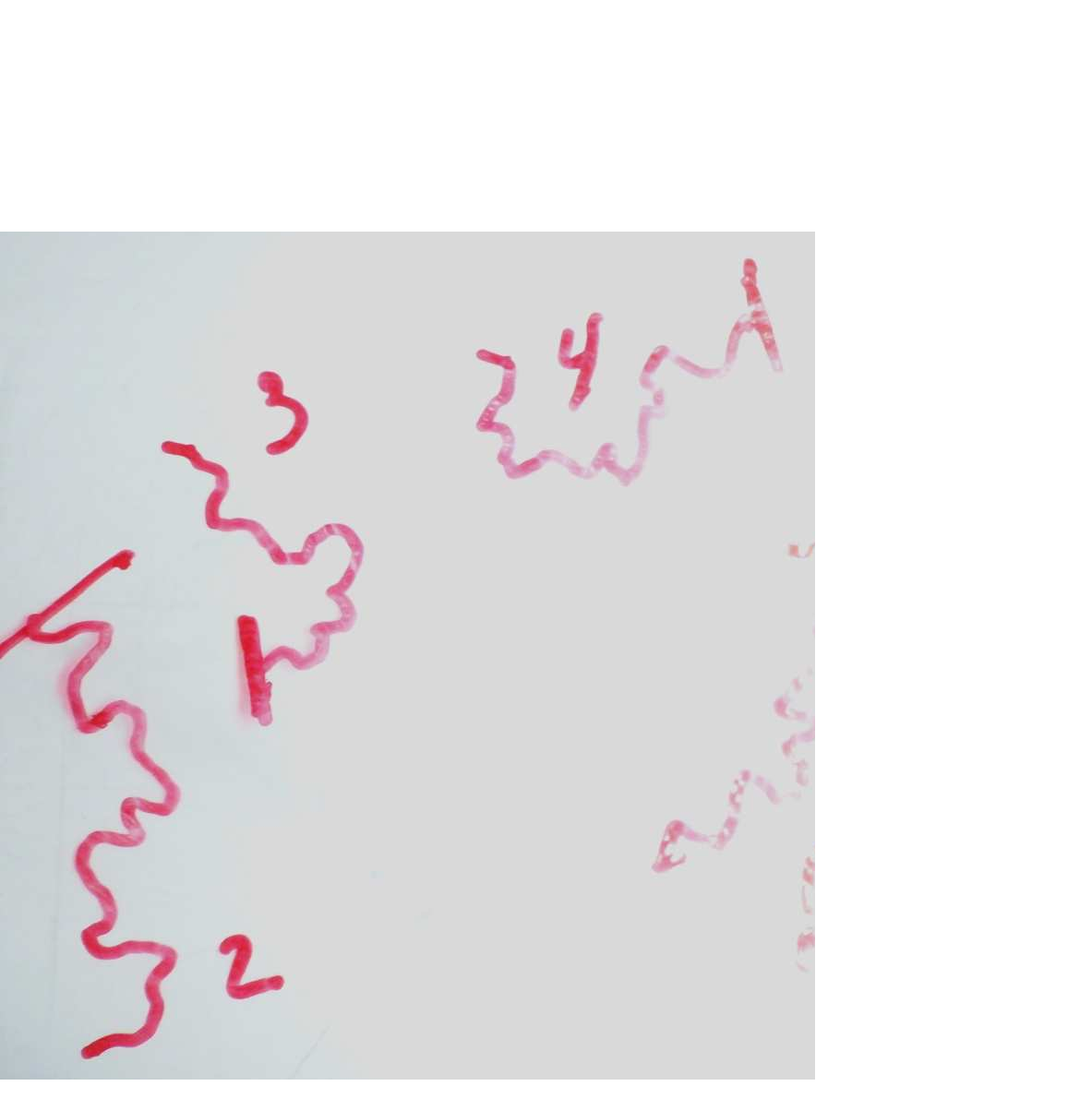

Figures 2. Visualisation of motion, movements
Collected results and their conclusions allowed are the following:

The intensity of the ambient electromagnetic field was measured using a magnetometer “ Electrosmog TES 92-meter” equipped with a probe of from 50 MHz to 3.5 GHz; EM field average was 7.5 millivolts / m.
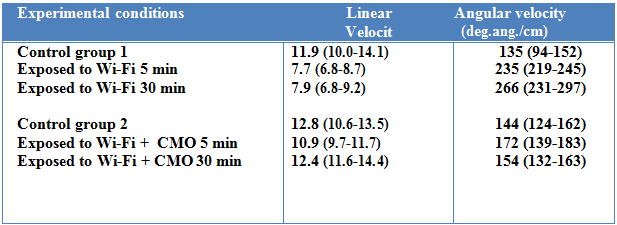
The linear speed values (11.9; 12.8) and angular (135, 144) obtained during one and the other of the two controls are statistically identical. The results of experiments performed then so are perfectly comparable.
The intensity of the electromagnetic field prevailing in the vicinity of the Wi-Fi enabled router was 500 millivolts / meter.
The linear speed values (7.7; 7.9) and angle (235, 266) exposed ants 5 or 30 minutes to Wi-Fi enabled differ highly significantly (P <0.001) values
controls. The Wi-Fi so decreases the ants travel speed and increases winding.
Evolution with the exposure time: the linear velocity values obtained after a part 5 min and the other 30 minutes of exposure did not differ statistically while those of the sinuous differ just not significant (0.05 <P <0.1). The Wi-Fi enabled impact thus increases over time.
The intensity of the electromagnetic field prevailing in neighboring Wi-Fi enabled with the CMO protection was also 500 mV / m.
The Wi-Fi therefore continues to operate 'as if nothing had happened'; CMO protection does not interfere with its operation. In short, the protection device CMO (with ultra-low intensity EM compensation signal), which 'correct' the biologically disturbing signals emited by the Wi-Fi enabled alone, so it is expected that the observed stress effect on exposed ants vanishes due to the CMO compensation effect.
After 5 minutes, the linear velocity values ants exposed to Wi-Fi and protected by CMO protection still differ from control values but at P <0.01; those of the sinuous differ statistically more control values ((0.05 <P 0.10). protection therefore clearly but not totally.
After 30 minutes, the linear velocity values ants exposed to Wi-Fi and protected by CMO protection not differ at all control values (NS). Those of the winding are even closer control values than were the values obtained after 5 min of exposure (P> 0.10). The stress effect of Wi-Fi radiation protection offset by the CMO is now very small, insignificant. The effectiveness of protection increases with time; after 30 min, it is about a little over 94% (see Tables 1 and 2).
Table 2. Evaluation in percentage of the linear and angular speed of the changes occurring during exposure (5 and 30 min) to a WiFi turned ON and the same Wifi turned OFF with a CMO protection.
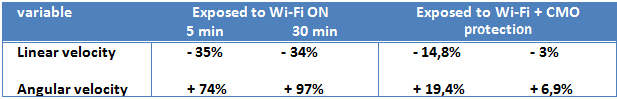
The present work shows that after exposure for 5 min and 30 min to a Wi-Fi router enabled, the linear velocity of ants decreased by 35% and 33% respectively while their angular velocity (= winding) increased by 74% and 97%. Ants come to wind (sinusoidal displacement) almost there and finally are no longer even able to move. It is therefore clear that a Wi-Fi activity induces stressful effects on these organisms. Based on the reactions of the ants, one can infer that their nervous system is affected by the EM radiation. This is also what we found at the end of our two previous works in the field: under the influence of electromagnetic waves, the ants are no longer responsive to behavior conditioning, and they lose all memory (Cammaerts at al., 2012b), they are almost no more responsive to their own pheromones and stop to harvest any more food (Cammaerts et al,
2012C, in press). Other physiological disturbances then are observed. The irradiated ants are in a state of 'stress' (broadly defined), what also say other researchers who have worked on a variety of living organisms (plants, rats ...) (Ledoigt 2007; Adang, 2009). In fact, electromagnetic waves interfere with the operation of biological structures, in particular the membrane unit; they therefore affect the mechanisms for nerve impulses, the functions of mitochondria, chloroplasts etc ....
It is unthinkable and impossible not to use communication technologies with so powerful radio frequencies. But the only solution is to develop means of protection against the potential adverse biological effects.
The present work shows that placing a M04 CMO protection near the antenna of a Wi-Fi enabled,
1) after 5 min of exposure, the linear speed of ants is not smaller than 15% and their angular speed increases more than 19%, which is low,
2) After a 30 min exposure, the linear speed is identical to the controls and the angular no longer increases by 7%, which is negligible. Ants have, moreover, a perfectly normal behavior then. The CMO protection used is perfectly effective! Its protective efficacy increases over time, even more so than increases, meanwhile, the stressful effects of wireless radiation.


The impact of waves on the cell membrane of ants and protozoa proves that the nervous system of human beings, consisting of similar cells, can also be affected.
Finally, the use of Wi-Fi equipment without protection seems to say the least hazardous. Wi-Fi radiation have adverse effects on every surrounding living because they generate electromagnetic fields disrupting biological mechanisms. It is most beneficial to guard against these harmful effects and to use an effective protective biotechnology. One tested here experimentally (CMO biotechnology), proves to be effective. In other words, a promising solution is to place near the antenna for Wi-Fi routers a CMO compensator (whose effectiveness has been proven experimentally) that restores by his presence (bio-technology Comosystems) system, waves compatible with the living. Adding that such protection does not impair the proper functioning of Wi-Fi, measurements of electromagnetic fields in support.
Références bibliographiques:
Adang,D., Renade, C. Vorst, A.V. (2009). Results of a long-term low-level microwave
exposure of rats. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 57: 2488-
2497.
Benlaidi, F. Z., El Kharroussi, M. (2011). Effets des ondes électromagnétiques générées par le GSM sur la mémoire et le comportement chez le rat. http://sites.google.com/site/9drineuro/r%C3%A9sum%C3%A9s6
Cammaerts, M.-C., Debeir, O., Cammaerts, R. (2011). Changes in Paramecium caudatum
(Protozoa) near a switched-on GSM telephone. Electromagn. Biol. Med., 30: 57-66. Cammaerts M.-C., Morel F., Martino F. & Warzée N. (2012a). An easy and cheap software-
based method to assess two-dimensional trajectories parameters. Belg. J. Zool.,in press.
Cammaerts M.-C., De Doncker P., Patris X., Bellens F. ,Rachidi Z. & Cammaerts D. (2012b).
GSM 900 MHz radiations inhibits ants’ association between food sites and
encountered cues. Electromagn Biol Med., 31: 151-165. DOI:
10.3109/15368378.2011.624661
Cammaerts M.-C., Rachidi Z., Bellens F &. De Doncker P. (2012c). Responses to
pheromones and food collection in an ant species under the influence of electromagnetic waves. Electromagn Biol Med., in press.
Everaert, J., Bauwens, D. (2007). A possible effect of electromagnetic radiation from mobile phone base stations on the number of breeding house sparrows (Passer domesticus). Electromagn. Biol. Med., 26: 63-72.
Favre, D. (2011). Mobile phone-induced honeybee worker piping. Apidologie, Springlink.com DOI: 10.1007/s13592-011-0016-x Goodman, R (2003). Effects of mobile phone radiation on reproduction and developpement in
Drosphila melanogaster.Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 89:48-55
Ledoigt, G. (2007). Etudes sur les effets des ondes du portable sur les végétaux - Université Blaise Pascal de Clermont-Ferrand - Sept. 2007. Orendaeova, J., Raeekova, E., Orendae, M. et al., (2009). Immunohistolochemical study of postnatal neurogenesis after whole-body exposure to electromagnetic fields: evaluation of age- and dose- related changes in rats. Zeitschrift Cellular and molecular Neurobiology,
29: 981-990. ISSN 0272-4340 (print); 1573-6830 (on line).
Panagopoulos, D. J., Karabarbounis, A., Margaritis, L. H. (2004). Effect of GSM 900-MHz mobile phone radiation on the reproductive capacity of Drosophila melanogaster. Electromagn. Biol. Med., 23: 29-43.
Sharma, V. P., Kumar, N. R. (2010). Changes in honeybee behavior and biology under the influence of cellphone radiations. Current Science 98, 1376-1378.
Wang, L., Peng, R., Hu, X. et al., (2009). Abnormality of synaptic vesicular associated proteins in cerebral cortex and hippocampus after microwave exposure. Synapse (New York), 63: 1010-1016.




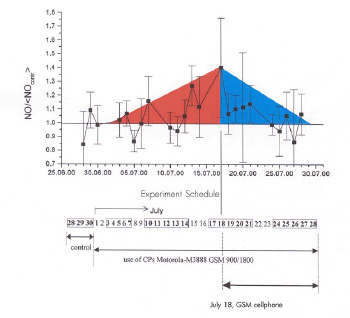
Exhaled nitric oxide
The nitric oxide (NO) found in an individual's expired air is a marker for tissue inflammation, cell dam- age and biological stress.
This pilot study was conducted with subjects who had not used a mobile telephone prior to the trial. The trial recorded 40% greater exhaled nitric oxide levels in unprotected mobile telephone users com-
pared to the normal levels. This increase was observed after 15 days use of the mobile telephone and
is a clear sign that this equipment is incompatible with the human body.
When compensatory oscillation is used (CMO fixed to the mobile telephone) the exhaled nitric oxide levels return to normal. This demonstrates that the mobile telephone can be made biocompatible with the human body if it is fitted with a CM
.
Stepanov E, 2001 - General Physics Institute, Moscow, Russia
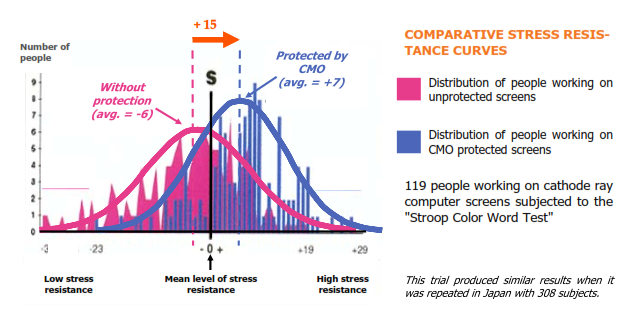
Work performance: rapidity, vigilance, concentration
The Stroop Color Word Test is used internationally by major companies and armies. It quantifies the ability of an individual to resist the stresses caused by the interference between conflicting informa- tion. This ability requires rapidity, vigilance and concentration.
People working with CMO-equipped screens have a statistically significant 15% improvement in their stress resistance compared to when they were working with screens without CMO. This result shows that the computer screen's electromagnetic field generates a stress on the human body and reduces its work performance.
The presence of compensatory oscillation (CMO) therefore increases the work performance of each individual who has a CMO-equipped computer screen by compensating the stress effects of this elec- tromagnetic source.
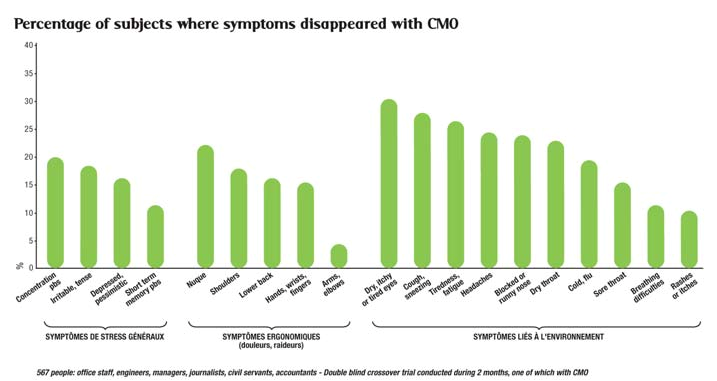
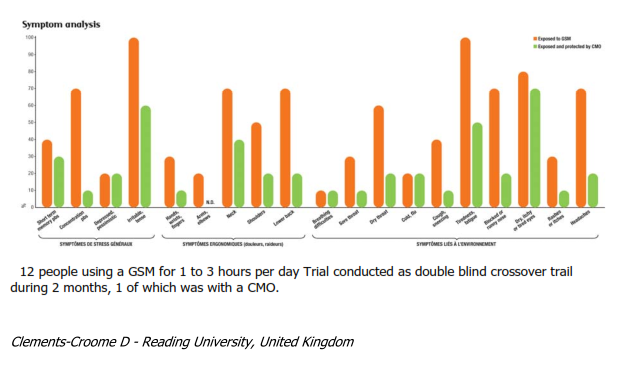
a) Electromagnetic stress symptoms caused by computer screens
The stress symptoms studied in this protocol (Building Sickness Syndrome) are usually related to er- gonomic and environmental factors and the general stress of working in company offices. It seems as if chronic exposure to the radiation from computer screens can cause the same type of neurophysical, functional and inflammatory symptoms.
This trial was conducted as a double blind (with a placebo*) crossover study (with or without CMO).
The difference between the CMO protected group and the unprotected group is that 35% of the stress symptoms observed in computer screen users have statistically disappeared when the users have compensatory oscillation (CMO). This demonstrates the presence of an electromagnetic stress in of- fices which is, on its own, responsible for 35% of the symptoms that are usually recorded and which are caused by regular exposure to radiation from computer screens.
* dummy: empty and inactive CMO
b) Electromagnetic stress symptoms caused by mobile telephones (GSM)
As in the previous trial, the stress symptoms studied in this protocol are usually related to ergonomic and environmental factors and the general stress of working in company offices. It seems as if chronic exposure to the radiation from GSM can cause the same type of neurophysical, functional and inflam- matory symptoms.
This trial was conducted as a double blind (with a placebo*) crossover study (with or without CMO). The difference between the CMO protected group and the unprotected group is that 51% of the stress symptoms observed in GSM users have statistically disappeared when the users have compensatory oscillation (CMO). This demonstrates the presence of an electromagnetic stress which is, on its own, responsible for 51% of the symptoms that are usually recorded and which are caused by regular ex- posure to radiation from GSM.
* dummy: empty and inactive CMO
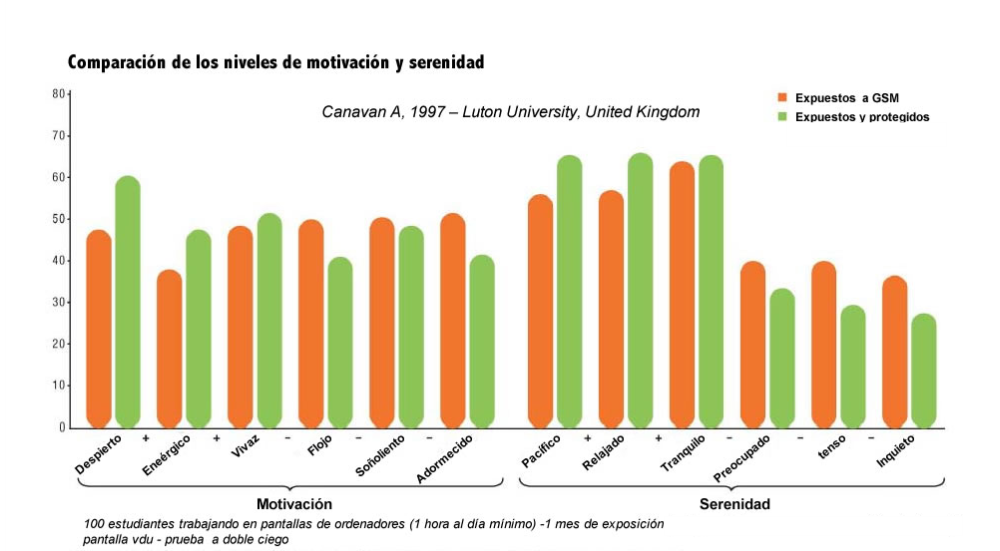
Motivation and serenity
Low intensity electromagnetic fields (EM) emitted by viewing screens change their users' EM environ- ment, which can effect brain function and results in a changed psychological status. Professor Ca- navan, a neuropsychiatrist, evaluated the psychological and emotional status of 100 students at his university working with cathode ray computer screens using the "Mood Test".
Motivation and serenity levels* were increased by 48 (166%) and 46.8 (77%) points respectively in students protected by CMO compared to unprotected students (with a placebo**).
The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) therefore greatly improved the psychological status of people working with cathode ray computer screens by making the EM environment biocompatible.
* see the quantification methods under the graphic.
**dummy: empty and inactive CMO
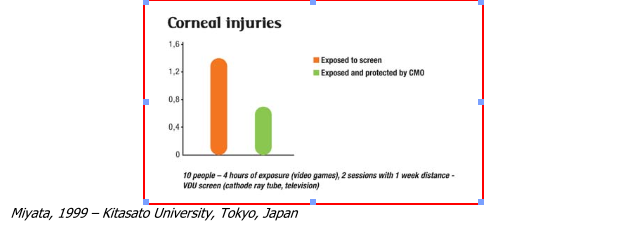
Corneal trauma
Professor Miyata's (Japan) work in man and animals on the effects of electromagnetic fields on the eye and vision have shown that ocular problems in users of screens and certain pathologies are due in part to the screen's electromagnetic fields and not just the luminosity and contrast.
In practice, screen filters do not protect the eye or sight against electromagnetic radiations even though they may provide some visual comfort (flickering, brightness).
This trial showed that micro-ulcerations develop on the cornea after 4 hours of continuous video gam- ing on a television screen (subjects at 1.20 metres from the screen).
The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) reduced corneal ulcerations by 50%
o Micro-ulcerations and corneal infection (keratitis)
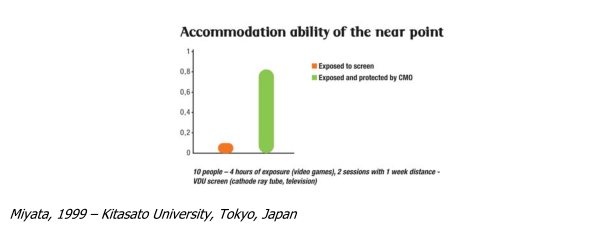
Eye's accommodation ability
Electromagnetic fields from viewing screens are partly responsible for ocular problems in people using this equipment.
In practice, screen filters do not protect the eye and sight against electromagnetic radiations because the filters do not make the viewing screens biocompatible for the user.
In this trial, using a compensatory oscillator (CMO) increased the accommodation ability of protected subjects by a factor of 10 whilst also reducing the observed ocular fatigue.
o Ocular fatigue
o Poor accommodation ability
Miyata, 1999 – Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan
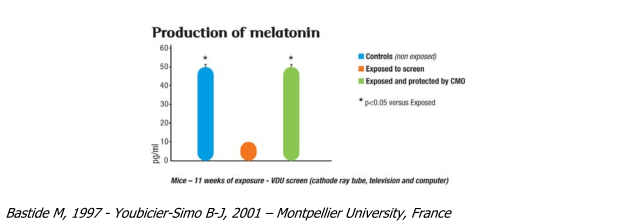
Melatonin production
Melatonin is a hormone that regulates sleep and stimulates the immune system. It has anti-radical and anti-tumour properties. This hormone is known to be electromagnetic sensitive.
The virtual cessation of Melatonin production under the influence of an electromagnetic field shows the inability of exposed animals to manage their electromagnetic stress. The resulting oxidative stress is due to a reduced anti-oxidant activity or an increase in the number of free radicals. It can cause several types of damage to cells, including cell death.
The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned Melatonin levels to normal.
o Sleeping problems
o Tiredness, depression
o Accelerated oxidative stress
o Premature ageing
o Increased epileptic crises
o Acceleration of pre-existing tumoral processes
Bastide M, 1997 - Youbicier-Simo B-J, 2001 – Montpellier University, France
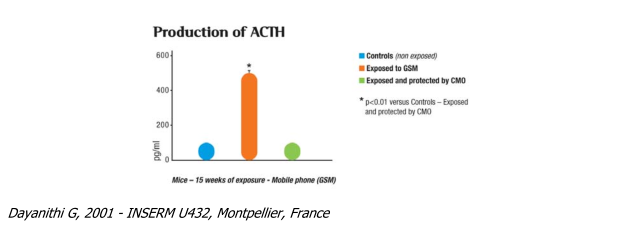
ACTH release from pituitary cells
ACTH (adreno-cortico-tropic hormone) is a stress hormone. It is secreted by the anterior hypophysis (anterior pituitary gland) in response to information received by the central nervous system. Its role is to stimulate the secretion of other hormones, especially cortisol (see later).
Abnormal variations in blood ACTH and glucocorticoid (Corticosterone, Cortisol) levels are sympto- matic of a state of stress (ACTH = stress marker).
A 400% increase in ACTH levels in animals in an electromagnetic field is an unequivocal observation of considerable stress provoked in the body by the radiation ("electromagnetic stress").
The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned levels to normal of this hormone which is an essential indicator of the hormono-immune system regulation.
Nervous and muscular systems:
o Psychic instability, irritability
o Tendency for depression
o Muscle weakness, contractures
Immune system:
o Reduced defences against bacteria, virus, parasites, allergies
o Aggravation of inflammatory diseases
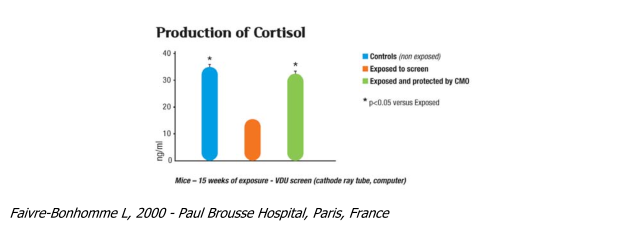
Cortisol production in the adrenal glands
Cortisol is an adrenal (above the kidneys) hormone that regulates the immune system. Its production is stimulated by the hypophysis (pituitary gland), a gland in the brain that is the control centre for hormones and immunity which are themselves interrelated.
Its production is controlled by ACTH and varies throughout the day. Its role is to regulate sugar, lipid, protein, ion and water metabolism to limit any sudden changes in the body's physiological balance. It is involved in stress management and inflammatory processes.
This trial showed a 57% reduction in Cortisol production in mice exposed to radiation from a cathode ray computer screen. The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned levels to almost normal (reduction limited to only 8%).
o Metabolic changes (sugars, fats, proteins)
o Inflammations
o Changed ion metabolism
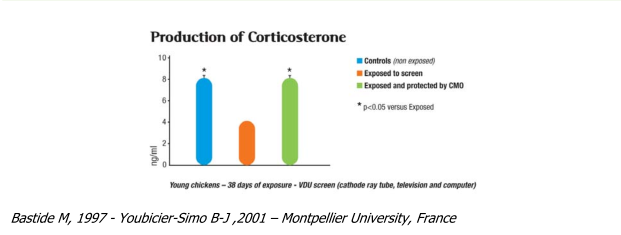
Corticosterone production in the adrenal glands
Corticosterone is an adrenal (above the kidneys) hormone that regulates the immune system. Its pro- duction is stimulated by the hypophysis (pituitary gland), a gland in the brain that is the control centre for hormones and immunity which are themselves interrelated.
This trial showed a 50% reduction in Cortocosterone production in animals exposed to radiation from a cathode ray computer screen or a television.
The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned levels to normal
o Deregulation of the immune system, reduction in bacterial, viral, defences, etc.
o Deregulation of the nervous and muscular systems: psychic instability, cramps, etc.
Bastide M, 1997 - Youbicier-Simo B-J ,2001 – Montpellier University, France
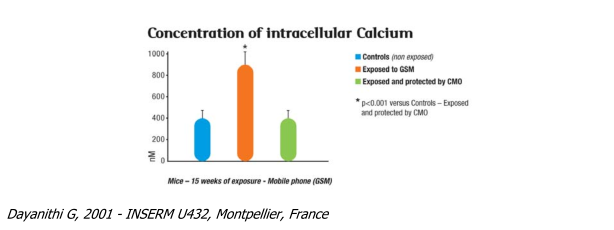
Calcium concentration in hypophyseal cells
Calcium (Ca++) plays an essential role in all cellular exchanges, especially in nervous tissue. It is an important mediator ("second messenger") in most cellular biochemical reactions. The hypophysis (brain gland) is a hormone control centre. Calcium and ACTH (see page 17) are essential components in the regulation of the hormono-immune systems.
Stress observed in subjects exposed to radiation from a mobile telephone provokes a strong perturba- tion of intracellular calcium that forces the body to use its re-balancing mechanisms. This provokes great cellular stress and results in the displacement of other ionic charges (Magnesium Mg++) that are critical for the metabolism. The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned calcium levels to normal.
o Changes to the activity of cellular enzymes activity (including transduction of signals)
o Displacement of ionic charges (cellular stress)
o Changed metabolism, spasmophilia
o Hormonal deregulations (thyroid, adrenal, ovaries...)
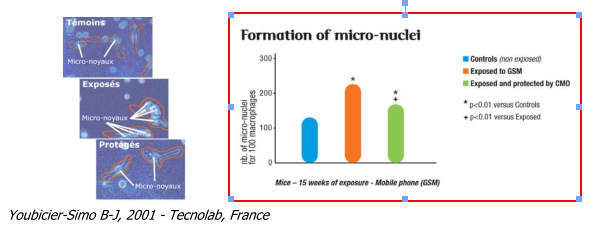
Formation of DNA micro-nuclei
An increased rate of formation of micro-nuclei in immune system cells (lymphocytes - macrophages) can indicate that there is a malfunction in the cellular cycle, cell death (apoptosis) or carcinogenesis (cancer development).
The trial involved the microscopic counting of the number of DNA fragments present in peritoneal macrophages (white blood cells, immune system cells) in exposed animals. The presence of these micro-nuclei in the cells are a possible first stage in carcinogenesis if these abnormal cells are not eliminated by the body' defence mechanisms. The large number of cells containing several DNA frag- ments in individuals exposed to a mobile telephone is clear evidence of the effects of its radiation at a fundamental level of the biological system. A compensatory oscillator (CMO) reduced micro-nuclei formation by 61%. The virtually normal level obtained corroborates the results for embryonic death described later (see page 26).
o Cell death (apoptosis)
o Cancer development (uncontrolled development of abnormal cells)
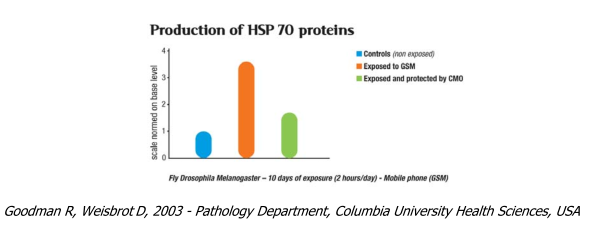
HSP 70 protein synthesis
An increase in synthesis of the stress protein HSP 70 is a sign of cellular stress (and also of the hyper- activation of the DNA's SRE sequence – see page 23). It shows that a factor that is toxic for the body is present. The stress protein HSP 70 is considered to be a significant marker for evaluating environ- mental pollution.
The test involves quantifying HSP 70 synthesis in the living systems studied which are exposed to electromagnetic radiation from a mobile telephone.
The trial results provide objective data of a large cellular stress linked to exposure. The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) reduced HSP 70 by 73% compared to the increase seen in exposed subjects.
o Auto-immune diseases
o Infectious diseases
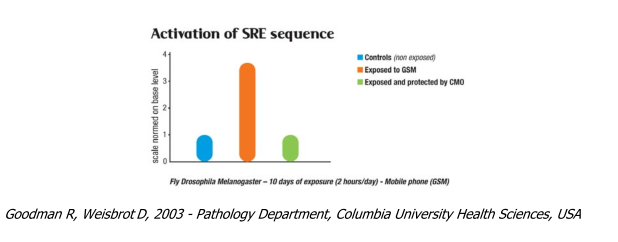
Activation of the DNA SRE sequence
Hyperactivation of the DNA's SRE sequence is a sign of DNA cellular stress (as is an increase in the levels of the stress protein HSP 70 – see earlier). The c-myc, c-fos and c-jun genes play an important role in regulating and controlling the body's development and are known to be involved in carcino- genic cell changes. These genes control cellular growth via the DNA's regulatory sequence called SRE, Serum Response Element.
The test involves quantifying SRE hyperactivation in the living systems studied which are exposed to electromagnetic radiation from a mobile telephone. This hyperactivation promotes cell proliferation and could promote carcinogenesis.
The trial results provide objective data of a large cellular stress linked to exposure. The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned SRE to normal.
o Carcinogenesis (uncontrolled cell proliferation)
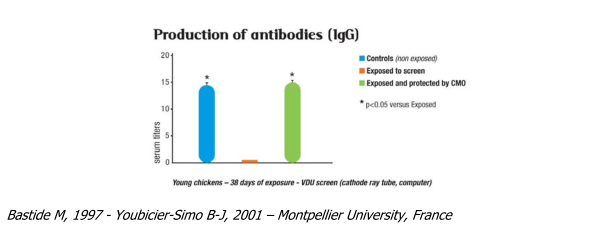
Antibody production
The antibodies evaluated (Immuno-globulin G - IgG) in this trial are defence molecules produced by the body to combat any foreign molecule. An immune system depression creates favourable condi- tions for chronic, relapsing or benign infections to develop (e.g. head colds) and can be an aggravat- ing factor in people who already have fragile health ("sanitary sentinels").
The virtual cessation of production (-95%) of IgG antibodies in young chickens exposed to radiation from a cathode ray screen demonstrates the important effect that electromagnetic fields have on the body which provoked an immune system collapse in the subject studied. The presence of a compen- satory oscillator (CMO) returned antibody levels to normal.
o Chronic benign infections (colds, etc.)
o Fragility in slow virus carriers (HIV, etc.)
Bastide M, 1997 - Youbicier-Simo B-J, 2001 – Montpellier University, France
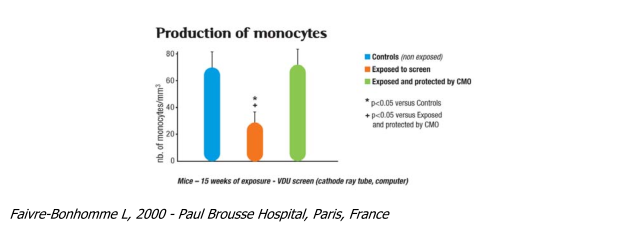
Monocyte production
Monocytes are white blood cells. They enter different tissues where they change into macrophages
(basic role in immunity: eat bacteria at the site of an infection, repair tissues, attack viruses, ...).
As for the antibodies previously discussed, a depression of the immune system creates favourable conditions for chronic, relapsing or benign or more serious infections to develop (e.g. head colds)
The large reduction (-58%) in monocyte production in mice exposed to radiation from a cathode ray screen demonstrates the important role of electromagnetic radiation on the body, which, in this trial, greatly weakens the immune system. The presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returned mo- nocyte levels to normal.
o Chronic benign infections (colds, etc.)
o Fragility in slow virus carriers (HIV, etc.)
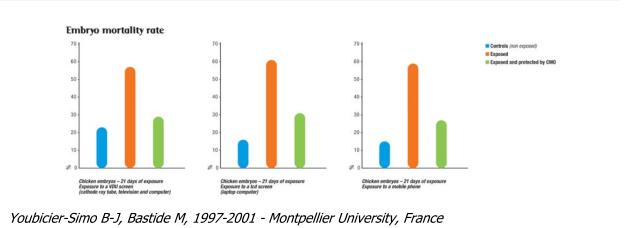
Embryonic death
Evaluating embryonic death in a living creature reveals the anomalies that arise during its develop- ment that lead to its death. Chick embryos are considered to be one of the living systems that are most sensitive to environmental risks including those from artificial electromagnetic fields.
The strong increase in embryonic death observed in this trial is a sign of the extreme toxicity of elec- tromagnetic radiation in electrical and electronic equipment such as computer screens (flat LCD and cathode ray tube) and mobile telephones.
This trial demonstrates that even when permanently exposed (which causes the death of most of the control group of embryos), the presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) allows vital processes to be protected or maintained and results in a virtually normal mortality rate.
o Possibility of spontaneous abortion in women
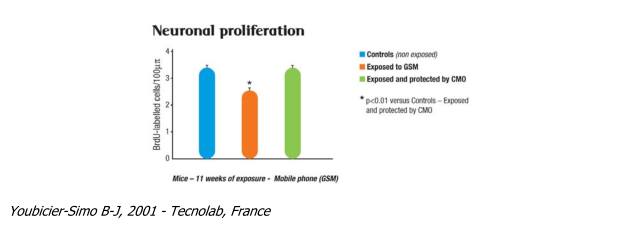
Neuronal proliferation in the hippocampus
The hippocampus is involved in short-term memory and learning mechanisms. A reduction in neurone proliferation (neurogenesis) in the hippocampus or a problem of their renewal can lead to problems with these mechanisms/functions.
In addition, a long-lasting reduction in neurone proliferation in the hippocampus during an individual's development period could lead to an atrophied hippocampus in the adult.
This pilot study demonstrates a 25% reduction in neurone proliferation in the hippocampus in mice exposed to radiation from a mobile telephone. Inversely, the presence of a compensatory oscillator (CMO) returns the neuronal development studied to normal.
o Troubles with short-term memory
o Hippocampus atrophy is a clinical sign of Alzheimer's disease
Youbicier-Simo B-J, 2001 - Tecnolab, France
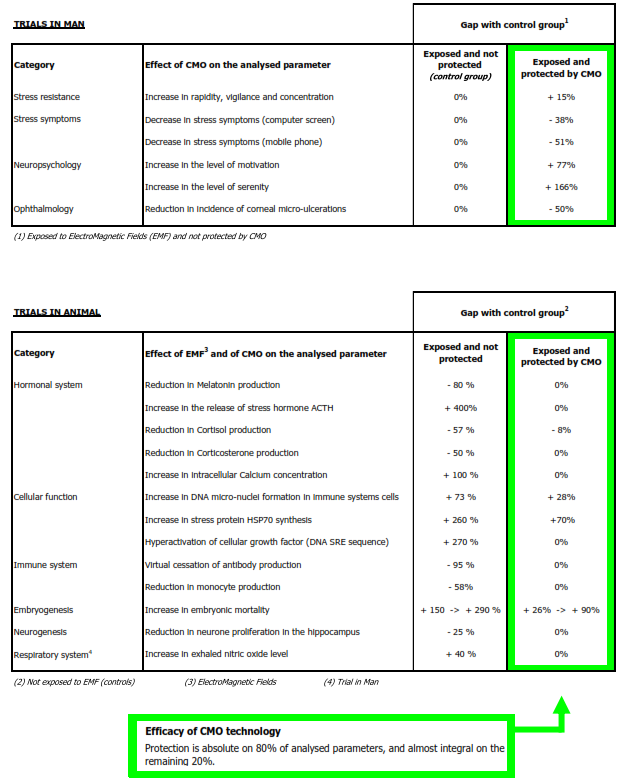
Summary table of trial results




Maurice FILLION-ROBIN
General Manager, TECNOLAB Research Centre,
av. de l'Europe, ZAC de la Thalie, 71100 Chalon-sur-Saône, France
Director of research into fundamental biophysics of electromagnetic biocompatibility (1991-2001) and technological development (patent for compensation magnetic oscillators)
Co-author of publications:
o Fillion-Robin M., Marande J.L., Limoni C., "Protective effect of Tecno AO antenna against VDU electro- magnetic fields as a stress factor", EBEA, 1996 ;
o V.N. Binhi, M. Fillion-Robin and G. Picard, "Physical constraints specifying possible primary mechanism whereby Tecno AO and superweak EMFs affect biological systems"; BEMS, 1998
o M. Fillion-Robin, A. Akimov, V.N. Binhi, "Tecno AO technology: Biological effects of EM and torsion fields". PIERS, 1999
o B.J. Youbicier-Simo, R. Messagier, M. Fillion-Robin, "Review of studies validating the protective efficacy of a new technology designed to compensate potential adverse bioeffects caused by VDU and GSM cell phone radiation". Radioprotecçao, The Journal of the Portuguese Society for Radiation Protection (IRPA) Vol.1 Nos. 8 and 9: 105-123, 2001
o V.N. Binhi, M. Fillion-Robin, "Biological effects of hyperweak electromagnetic fields : Present safety stan- dards conflict with reality" In publication
o V.N. Binhi, M. Fillion-Robin1 and E.V. Stepanov2, "Effect of Tecno AO protection on concentration of ex- haled nitric oxide in humans".
1 - Tecnolab Research Centre, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France
2 - General Physics Institute RAS, Moscow, 117942 Russia
Pr. Vladimir N. BINHI
PhD. in Mathematics and Physics
Head of Electromagnetic Biophysics Laboratory,
General Physics Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences,
38, Vavilova St., Moscow 119991, GSP-1, Russia
Consultant, Director of Physics and Biophysics Department, Tecnolab Research Centre, France
Expertise: Quantum physics
Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Official WHO correspondent for Russia
Magnetic processes in molecular systems
Proton dynamics and structure defects in liquid water
Theoretical modelling of biological effects of electromagnetic fields
Magnetic measurements
Peer-reviewed international publications since 1990: 24
Abstracts, preprints, reports: 34
Author of a book on theoretical biophysics:
"Magnetobiology: Underlying Physical Problems" published by Academic Press, London, 2002

Dr. René MESSAGIER
Doctor of medicine
General practitioner
Medical Research Director, Tecnolab Research Centre
Author of a literature review:
o "Synthèse : Champs électromagnétiques et Biologie."
European BioElectromagnetics Association (EBEA) congress, 1996 Nancy, France
Peer reviewed publications:
o Co-author: B.J. Youbicier-Simo, R. Messagier, M. Fillion-Robin,
Youbicier-Simo et al., 'Review of studies validating the protective efficacy of a new technology designed
to compensate potential adverse bioeffects caused by VDU and GSM cell phone radiation', Radioprotecçao, The Journal of the Portuguese Society for Radiation Protection (IRPA) 2001, Vol.1 Nos.
8 and 9: p105-123, 2001.
Prof. Yu.G. GRIGORIEV
Prof. Dr.MD Sc.
State Scientific Center of Russian Federation - Institute of Biophysics (SSCRF), Moscow, Russia Chairman of Russian National Committee on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (RNCNIRP) Member of the Academy of Sciences of Russia
 Dr. Benoît-Jules YOUBICIER-SIMO
Dr. Benoît-Jules YOUBICIER-SIMODoctor in Neurosciences
University Reader
Immunology and Parasitology Laboratory, Pharmacy Faculty, Montpellier 1 University,
15, av. de Flahault, 34060 Montpellier Cedex 1, France Biological Research Director, Tecnolab Research
Centre Expertise: neuro-endocrinology, immunology
Peer-reviewed international publications: 7
Peer-reviewed international publications on bio-electromagnetism: 3
B.J. Youbicier-Simo et al."Biological effects of continuous exposure of embryos and young chickens to electro- magnetic fields emitted by video displays units", Bioelectromagnetics 1997 Vol 18, N. 7: 514-523.
Bastide et al., "Etude toxicologique des rayonnemments électromagnétiques émis par les écrans de visualisation (TV, ordinateurs) et de téléphones cellulaires chez le poulet et la souris", Journées scientifiques: "Impacts sur l'homme des rayonnements ionisants et non-ionisants", Brest, France, 23-24 June 2000, Actes du Colloque, p181-
194.
B.J. Youbicier-Simo et al., 'Review of studies validating the protective efficacy of a new technology designed to compensate potential adverse bioeffects caused by VDU and GSM cell phone radiation', Radioprotecçao, The Journal of the Portuguese Society for Radiation Protection (IRPA) 2001, Vol.1 Nos. 8 and 9:
Participation in editing a scientific book: 1
International congresses with peer review: 15
 Prof. Madeleine BASTIDE †
Prof. Madeleine BASTIDE † Professor Emeritus in Immunology
Pharmacy Faculty – Immuniology & Parasitology Laboratory - Faculté de Pharmacie - Montpellier 1 University- France
Peer-reviewed international publications: 93 (1965 - 1997)
World renowned for her fundamental biological research on the effects of high dilutions and low doses and their possible mechanisms for biological information.
Since1993:
Director of studies conducted in conjunction with Dr B.J.Youbicier-Simo at Montpellier 1 University on the effects of magnetic fields on chickens and mice exposed to viewing apparatus and mobile telephones and their stan- dardisation using the magnetic oscillation compensation technology developed by Tecnolab (in 1991).
Peer-reviewed international publications from this work: 3 (1997-2000-2001)
 Dr. Laurence BONHOMME-FAIVRE
Dr. Laurence BONHOMME-FAIVREDoctor in Pharmaceutical Sciences
Hospital Pharmacist
Head of Pharmacy-Pharmacology Service - Paul Brousse teaching hospital, Paris, France
Associate professor, PARIS XI University, Paris, France
(1988-2000) Publications
o international journals: 54 / national journals: 8
o other international publications: 6 (1992-93)
(1987-2001) Congress communications
o international: 53 / on CEM: 18 since 1994
o national: on CEM: 6
Peer-reviewed international publications on CEM: 3 in 1995, 1998 and 2000
o effect of 50Hz in mice and man
o effects of exposure to TV on mice
in France in1997 - human cancer and ELFs
in 2000 - Danger of mobile telephones and their relay stations
 Prof. Anthony G. CANAVAN †
Prof. Anthony G. CANAVAN † B.A, M.Phil.,M.A., D.Phil., AFBPsS, C.Psychol. Professor of Clinical Psychology
Institute for Health Services Research (IHSR) University of Luton, UK
Professor and Research Director
Neurological Therapy Centre - Düsseldorf University Institute – Düsseldorf - Germany
Specialist in clinical neuropsychology
Subject taught: Research methods, Statistics, Neuropsychology, Clinical Psychology. Peer-reviewed international publications: 69
(1983 - 1997)
 Prof. Derek CLEMENTS-CROOME
Prof. Derek CLEMENTS-CROOMEBSc., MSc.,Ph.D., CEng., CPhys. Professor of Construction Engineering
Department of Construction Management & Engineering, University of Reading, Reading RG6 6AW, UK
2000: Awarded Lifetime Membership of the International Academy of Indoor Air Sciences
Editor and founder of:
International Intelligent Building Journal
1972-2000: Author of books on architecture, the environment and ergonomy at work as productivity factors:12
Latest publication: "Creating the Productive Workplace", 2000
Congresses, conferences: 105
Publications (1962 - 2000): 224
Dr. V.S. STEPANOV
Deputy Director
State Scientific Center of Russian Federation - Institute of Biophysics (SSCRF), Moscow, Russia
(WHO adviser)
 Prof. Gerald J. HYLAND
Prof. Gerald J. HYLANDPh.D. in Theoretical Physics
1998-2001 - Senior Lecturer in Theoretical Physics
Department of Physics, Warwick University, Coventry, UK
2001- Associate Fellow of Warwick University, Coventry, UK
1997- Member of the Executive Board of the International Institute of Biophysics, Neuss-Holzheim, Germany
1965- 91 - Work on biophysics with Prof. Herbert Fröhlich, F.R.S. 1985 "From Theoretical Physics to Biology : The Forward Path of Theory with Herbert Fröhlich"
International biophysics expert on the interaction of exogenous non-ionising CEM (MW) with the endogenous activity of coherent microwaves in living systems.
Government consultant on the potential risks of mobile telephones and their non-thermal health effects. Peer-reviewed international publications on bio-electromagnetism: 15
Current theories and research: Origins of 'coherent excitation' cerebral waves, biophotonic emissions and micro- waves at a cellular level; role of external CEM on EEG structure and spectrum; Creating of electromagnetic bio- compatibility.
(WHO adviser)
 Prof. Reba Goodman
Prof. Reba GoodmanProfessor of Pathology, Department de Pathology, Columbia University Health Sciences, 630 West, 168 Street, New York, USA
JOURNAL OF CELLULAR BlOCHEMlSTRY
VOL. 89, lssue 1, 2003, pages 48-55
"Effects of mobile phone radiation on reproduction and development in Drosophlia melanogaster"
Weisbrot David1, Lin Hana2, Ye Lin1, Blank Martin3, and Reba Goodman1
1- Department of Pathology, Columbia university Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. NewYork 100032
2- Department of Anatony, Columbia university Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. NewYork 100032
3- Department of Physiology, Columbia university Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. NewYork 100032
Dr. Jean-Luc MARANDE
Doctor of medicine
Specialist employment service doctor
Hospital doctor
Cochin-Tarnier Teaching Hospital Group, Paris, France
Congresses, conferences: 10
Peer-reviewed international publications: 13
1981- 97: Publications as part of the Comité d'Hygiène et Sécurité du Travail (health and safety at work commit- tee): 21
1989-95: Clinical pharmacology research work on hepatitis A, B and C in healthcare workers
Research work on CEM:
in 1986: The workplace risks of viewing screens
87/88/92/94 : Radioprotection in hospitals
95: Work on VDUs and secretaries
95: "Etude clinique de l'état de stress lié au travail sur écran et sa correction par une protection technique du
CEM de l'écran"
97: Report: Working with VDUs - implementation of Decree no. 91-451 (May 14th 1991)
 Prof. Mikio MIYATA
Prof. Mikio MIYATAProfessor of Medicine and Ophthalmology, Ophthalmology Faculty
1988-99 at Kitasato University of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan
since 1999 at the Environmental Medical Center, Kitasato Institute Hospital, Japan
Publications in Japan: 139
For his expertise on CEM and the eye:
1999 Member of the Japanese government Research Board into the 700 simultaneous cases of epilepsy in chil- dren caused accidentally on December 16th 1997 by a Pokemon video game during a national television broad- cast.
International publications:14
o "Experimental study on possibility of corneal injury by electromagnetic waves" Hippokrates Verlag
Stuttgart, S.Ishikawa et al; reprint p 87-99, 1995
o "Aggravation of allergic conjunctivitis possibly due to electromagnetic waves", Current Aspects in Oph- thalmology, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., p. 214-218, 1992

Dr. Marco Francisco PAYA
Doctor of medicineDirector of the IMI
Specilist pain and balance Clinic, Alicante, Spain
Specialist in the medical evaluation and treatment of pain
1986-98: Independent research on the theme of exogenous electromagnetic fields on the human body's endoge- nous fields.
Direction of theses, Paris XIII Faculty of Medicine, Paris, France
1999-2002: independent consultant and cordinator of Tecnolab medical trials,
Since 1999: Member of board of Comosystems S.L., Alicante, Spain, a company that is now manufacturing
CMO under an exclusive licence.
Dr. Govindan DAYANITHI
Doctor of medicine
Sensorial neurophysiology laboratory, U432 INSERM - 2, place Eugène Bataillo, Montpellier, France
 Marie-Claire CAMMAERTS-TRICOT
Marie-Claire CAMMAERTS-TRICOT
Chef de travaux mtricot@ulb.ac.be
Faculté des Sciences Campus du Solbosch CP160/12, avenue F.D. Roosevelt 50, 1050 Bruxelles BELGIUM
Unités de recherche / Evolution Biologique et Ecologie [Evolutionary Biology and Ecology] (EBE)
Projets : Biologie des Insectes Sociaux [Biology of Social Insects]
Laboratoire d’éco éthologie évolutive, CP 160/12 DBO Faculté des Sciences, Université Libre de Bruxelles 50, Av F. Roosevelt, 1050 Bruxelles.
******************
NB : Le laboratoire TECNOLAB a cessé ses activités de recherche en février 2002 et ses principaux collaborateurs sont réunis au sein de l'association CIRBE (Centre International de Recherche en Biophysique Electromagnétique)
NB: The TECNOLAB laboratory stopped its research activity in February 2002 and its main researchers are now re-united in the CIRBE association (Centre International de Recherche en Biophysique Electromagnétique - International Research Centre in Electromagnetic Biophysics)

International peer-reviewed scientific publications of experimental work on Compensatory Magnetic Oscillation [CMO] coordinated by TECNOLAB (Centre de Recherche en Biophysique Électromagnétique)
( CMO) Compensating Magnetic Oscillator Tecno AO [AO: Autonomous oscillators]
"Biological Effects of Continuous Exposure of Embryos and Young Chickens to Electro- magnetic Fields Emitted by Video Display Units"
B.J. Youbicier-Simo, F. Boudard, C. Cabaner, and M. Bastide,
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, University of Montpellier 1, France
BIOELECTROMAGNETICS, Vol 18, Number 7, 1997, pages 514-523
"Electromagnetic Biocompatibility at Workplace: Protection Principles, Assessment and Tests. Results of an EMF Protective Compensation Technology in Humans and in Animals" G J. Hyland1, D. J. Clements-Croome2
1 - University of Warwick, Coventry, UK and International Institute of Biophysics, Germany
2 - University of Reading, UK
PROGRESS IN RADIATION PROTECTION (IRPA Publication Series) NON IONIZING RADIATION, NIR
99, Vol 1, 1999, pages 213-242
"Ocular functions during loading by visual display terminal and the effect of (CMO) Tecno AO" Yayoi Satou, Akiko Hara, Kouji Oono, Hiromi Kikuchi, Hiroe Matsuzaki, Tatsuto Namba and Mikio Mi- yata
School of Medicine Kitasato University, 1-15-1 Kitasato, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, 228-8555, Japan
JAPANESE REVIEW OF CLINICAL OPHTALMOLOGY, Vol 11, Number 93, 1999, pages 1634-1637, 32-
35
"Computers and Health in the Workplace"
Derek J. Clements-Croome1, John Jukes2
1 - Department of Construction Management and Engineering, University of Reading, UK
2 - Jukes Association, Old Couldson, UK
HEALTHY BUILDINGS 2000: Exposure, Human Responses and Building Investigations, SYR INDOOR AIR, Vol. 1, 2000, pages 119-124
"Review of Studies Validating the Protective Efficacy of a New Technology* Designed to Compensate
Potential Adverse Bioeffects Caused by VDU and GSM Cell Phone Radiation" B.J. Youbicier-Simo, R. Messagier, M. Fillion-Robin,
Tecnolab Research Center, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France RADIOPROTECÇÃO (Radioprotection) The Journal of the Portuguese Society for Radiation Protection (IRPA), Vol I, Number 8 and 9, 2000-2001, pages 105-123, ISSN 874-7016
"Toxicologic study of electromagnetic radiation emitted by television and video display screens and cellular telephones on chickens and mice"
M.. Bastide1, B.J. Youbicier-Simo1-2, J.C. Lebecq1, J. Giaimis1
1 - Laboratory of Immunology and Parasitology, MENRT-EA 2413, College of Pharmacy, University of
Montpellier 1, France
2 - Tecnolab Research Centre, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France
INDOOR AND BUILT ENVIRONMENT, Vol. 10, Number 5, 2001, pages 91-98
"Video screen exposure and 6-sulfatoxymelatonin urinary excretion in women"
R. Santini1, R. Messagier2 , B. Claustrat3 , M. Fillion-Robin2 , B.J. Youbicier-Simo2
1 - Institut National des Sciences Appliquées (INSA), Bât. Louis Pasteur, 20 rue Albert Einstein, 69621
Villerbanne, France
2 - Tecnolab Research Centre, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France
3 - Hôpital Neuro-cardiologique, Service de radiopharmacie et de radioanalyse, Centre de Médecine
Nucléaire, 59 bd. Pinel, 69394 Lyon, France
PATHOLOGIE BIOLOGIE, Issue 51, 2003, pages 143-146
"Effects of mobile phone radiation on reproduction and development in Drosophila mela- nogaster"
Weisbrot David1, Lin Hana2, Ye Lin1, Blank Martin3, and Reba Goodman1
1 - Dept of Pathology, Columbia University Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. New York 100032
2 - Dept of Pathology, Columbia University Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. New York 100032
3 - Dept of Pathology, Columbia University Health Sciences, 630 West 168 St. New York 100032
JOURNAL OF CELLULAR BIOCHEMISTRY, Vol. 89, Number 1, 2003, pages 48-55 http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/issuetoc?ID=104088364
Papers on Compensatory Magnetic Oscillation [CMO] presented during international scientific congresses
CMO Tecno AO [AO: Autonomous oscillators]
"Biological effects of low dose radiations from TV set on embryos and young chickens:
study of a protective material"
F. Boudard, B.J. Youbicier-Simo, J.D. Baylé, M. Bastide
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, Unit of Endocrine Neurobiology, University of Mont- pellier, France
1993 - GIRI (Montpellier, France), pages 15-16, 71-72
"The biological effects of low doses of television emitted radiation in chick embryos and young chickens: a study of (CMO) Tecno AO protective equipment"
M.. Bastide, B. J. Youbicier-Simo, J. D Bayle
1994 - WWDU Work With Display Units (Milano, Italy), Annexe 1-8
"Protective effect of Tecno AO (CMO) antenna against VDU EMFs as stress factor"
M. Fillion-Robin1, J.L. Marande2, C. Limoni3
1 - Tecnosphere Research Centre 71150 Sampigny, France
2 - Occupational Health Medicine, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France
3 - SSQEA Ticino, 6830 Chiasso, Switzerland
1996 - MAGNETOTHERAPY (Royal Society of Medicine, London), pages 195-203
"Bioeffets of continuous exposure of embryos and young chickens to ELF displayed by desk computers: protective effects of Tecno AO antenna"
B.J. Youbicier-Simo, F. Boudard, C. Cabaner, M. Bastide,
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, University of Montpellier 1, France
1996 - EBEA European BioElectromagnetics Association (Nancy, France), pages 70, 144
"Improvement of psychotechnical performances and stress resistance after modulation of the VDT radiation by an oscillating magnetic field"
M. Fillion-Robin1, J.L. Marande2, C. Limoni3
1 - Tecnosphere Research Centre 71150 Sampigny, France
2 - Occupational Health Medicine, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France
3 - SSQEA Ticino, 6830 Chiasso, Switzerland
1996 - MAGNETOTHERAPY (Royal Society of Medicine, London), pages 195-203
"Physical constraints specifying primary mechanisms whereby Tecno AO and superweak
EMFs affect biological systems"
V.N. Binhi1, M. Fillion-Robin2 and G. Picard3
1 - International Institute of Theoretical and Applied Physics RANS, Russia
2 - Tecnolab Research Centre, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France
3 - Department of Analytical Chemistry, Turin University, 10125 Turin, Italy
1998 - BEMS (St.Pete Beach, Florida, USA), pages 30, 100-104, 138-139
"Mortality of chickens embryos exposed to EMFs from mobile phones"
"Damage of chickens embryos by EMFs from mobile phones: protection by a compensa- tion antenna"
B.J. Youbicier-Simo, J.C. Lebecq and M. Bastide
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, University of Montpellier 1, France
1998 - BEMS (St. Pete Beach, Florida, USA), pages 30, 100-104, 138-139
"kT Problem in Magnetobiology: The Present State of the Art and Perspectives of the So- lution"
V.N. Binhi - General Physic Institute RAS, Institute of Cell Biophysics RAS, Moscow, Russia
1999 – ELECTROMAGNETICS AND HUMAN HEALTH (Moscow, Russia), pages 250-251
"Tecno AO (CMO) Technology: Biological Effects of EM and Torsion Fields"
M. Fillion-Robin1, A.E. Akimov2, V.N. Binhi2
1 - Tecnolab Research Centre, ZAC de la Thalie, Av. l'Europe, 71100 Chalon Sur Saône, France
2 - International Institute of Theoretical and Applied Physics RANS, Russia
1999, PIERS Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium (Taipei, Taiwan), page 441
"Cortisol variations observed in mice placed in front of colour TV screen: a feed back con- trol"
"Haematological effects of low doses of television emitted-radiation in mice: a parallel study with a protective equipment"
L. Bonhomme-Faivre1, R. Santini2, S. Marion3, E. Bizi1, H. Auclair3, L. Bottius1, S. Orbach-Arbouys1, N.L. Bui2
1 - Service de Pharmacie, Laboratoire de Pharmacologie
2 - Laboratoire d'Hématologie, Hôpital Paul Brousse (Paris)
3 - Institut National des Sciences Appliquées (INSA), Laboratoire de Biochimie-Pharmacologie (Lyon- France)
1999 - BEMS - Bioelectomagnetics Society, Long Beach, California, USA, pages 41, 92
"Electromagnetic Biocompatibility at Workplace: Protection Principles, Assessment and Tests. Results of an EMF Protective Compensation Technology in Humans and in Animals" G J. Hyland1, D.J. Clements-Croome2
1 - University of Warwick, Coventry, UK
1 - International Institute of Biophysics, Germany
2 - University of Reading, UK
Progress in Radiation Protection (Publication Series), 1999 – NIR Non Ionizing Radiation (IRPA) (Co- logne, Germany), pages 213-242
"Mortality of chicken embryos continuously exposed under GSM cell phone and validation of the effectiveness of a protective device"
"Interference from GSM cell phone with the production of stress hormones in healthy and
Lewis Lung carcinoma-bearing mice: Effectiveness of a protective device."
B.J. Youbicier, B. Lebecq and M. Bastide
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, University of Montpellier 1, France
2000 -INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CELL TOWER SITING, (Salzburg, Austria), pages 233-235
"Cortisol alterations observed in mice placed in front of colour TV screen: a parallel study with protective equipment"
L. Bonhomme-Faivre1, R. Santini2, S. Orbach-Arbouys1.
1 - Service Pharmacie, Laboratoire de Pharmacologie, Hopîtal Paul-Brousse, 14 Avenue Paul Vaillant
Couturier-94800-Villejuif, France
2 - Institut National des Sciences Appliquées, Laboratoire de Biochimie-Pharmacologie, 20 Av. Albert
Einstein, 69621 Villeurbanne, France
2000 - BEMS Bioelectromagnetics Society (Munich, Germany), pages 250-251
"Computers and Health in the Workplace"
Derek J. Clements-Croome1, John Jukes2
1 - Department of Construction Management and Engineering, University of Reading, UK
2 - Jukes Association, Old Couldson, UK
2000 – HEALTHY BUILDINGS 2000: Exposure, Human Responses and Building Investigations. Pro- ceedings, Vol. 1, pages 119-124
"Sensivity of chicken embryos to portable computer radiation (LCD*) and protective ef- fectiveness validation of a compensation magnetic oscillator**"
* Liquid Crystal Display ** CMO technology
This study was conducted at the University of Montpellier (France) under the scientific and technical research agreement N° 98018 between the University of Montpellier and Tecnolab.

B. J Youbicier-Simo
Laboratory of Immunology, College of Pharmacy, University of Montpellier 1, France



















































 Dr. Benoît-Jules YOUBICIER-SIMO
Dr. Benoît-Jules YOUBICIER-SIMO Prof. Madeleine BASTIDE †
Prof. Madeleine BASTIDE †  Dr. Laurence BONHOMME-FAIVRE
Dr. Laurence BONHOMME-FAIVRE Prof. Anthony G. CANAVAN † B.A, M.Phil.,M.A., D.Phil., AFBPsS, C.Psychol. Professor of Clinical Psychology
Prof. Anthony G. CANAVAN † B.A, M.Phil.,M.A., D.Phil., AFBPsS, C.Psychol. Professor of Clinical Psychology Prof. Derek CLEMENTS-CROOME
Prof. Derek CLEMENTS-CROOME Prof. Gerald J. HYLAND
Prof. Gerald J. HYLAND Prof. Reba Goodman
Prof. Reba Goodman
 Prof. Mikio MIYATA
Prof. Mikio MIYATA
 Marie-Claire CAMMAERTS-TRICOT
Marie-Claire CAMMAERTS-TRICOT
